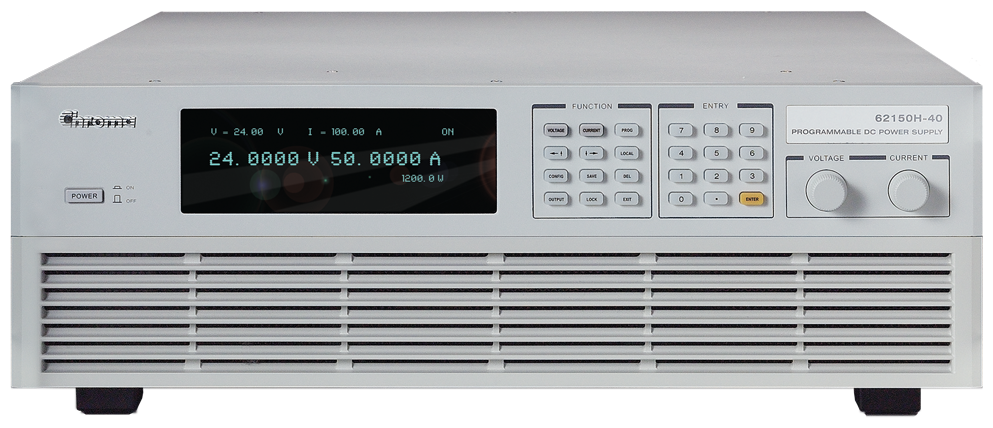
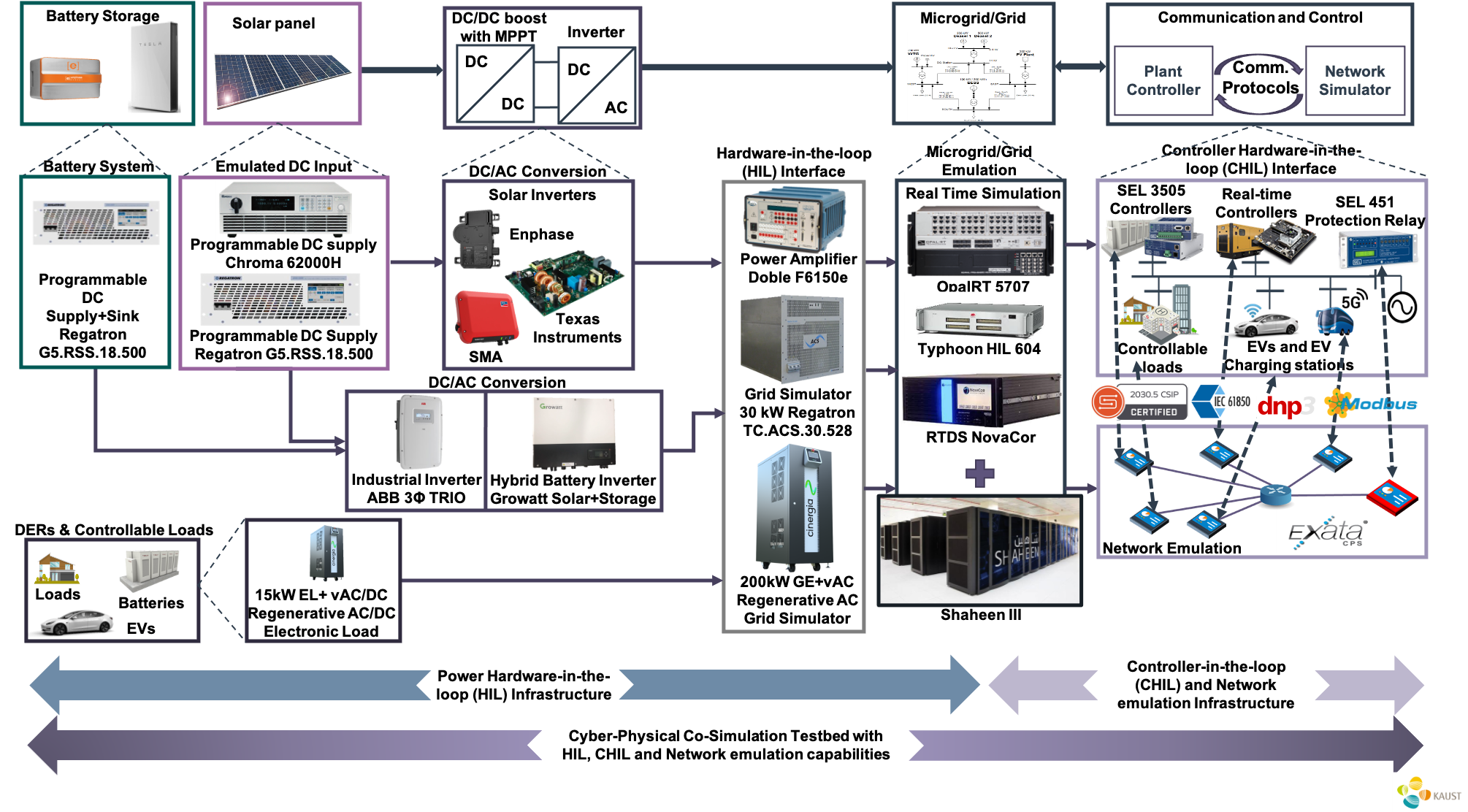
Real-time simulators
The real-time simulators mimic the physical system and provide the full system response. This produces a high fidelity representation of the transient and dynamic behavior of complex power systems.


Power amplifiers
Power amplifiers are employed for high speed and low latency closed loop communications for real time digital simulators. In real devices such as DERs, loads can be interfaced using a power amplifier for running power hardware in the loop (PHIL) studies.
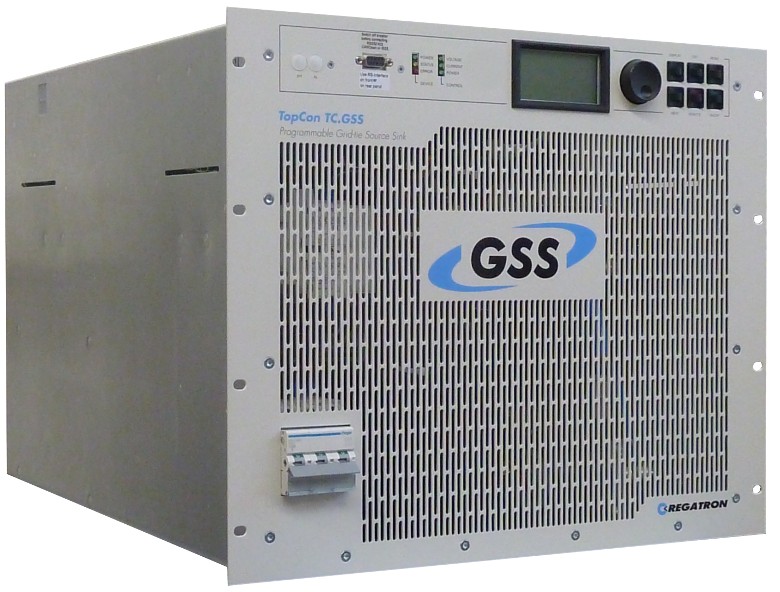


Grid simulation
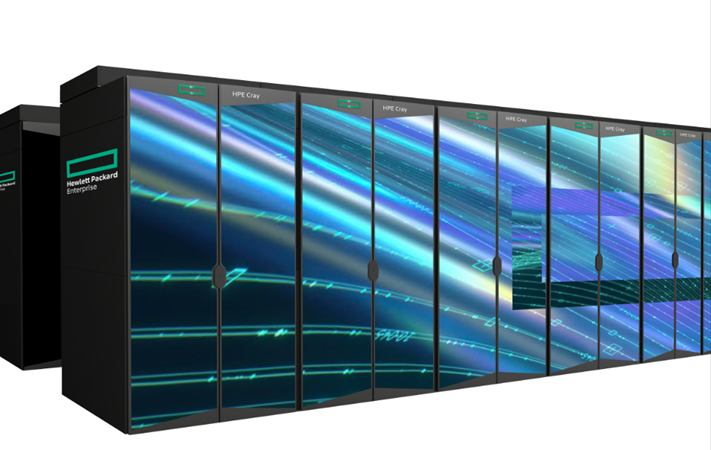
Grid simulators are capable of emulating varying grid conditions to facilitate the testing of grid-connected equipment, thereby visualize power system dynamics. This is achieved by combining real-time simulators with the Shaheem III supercomputer.

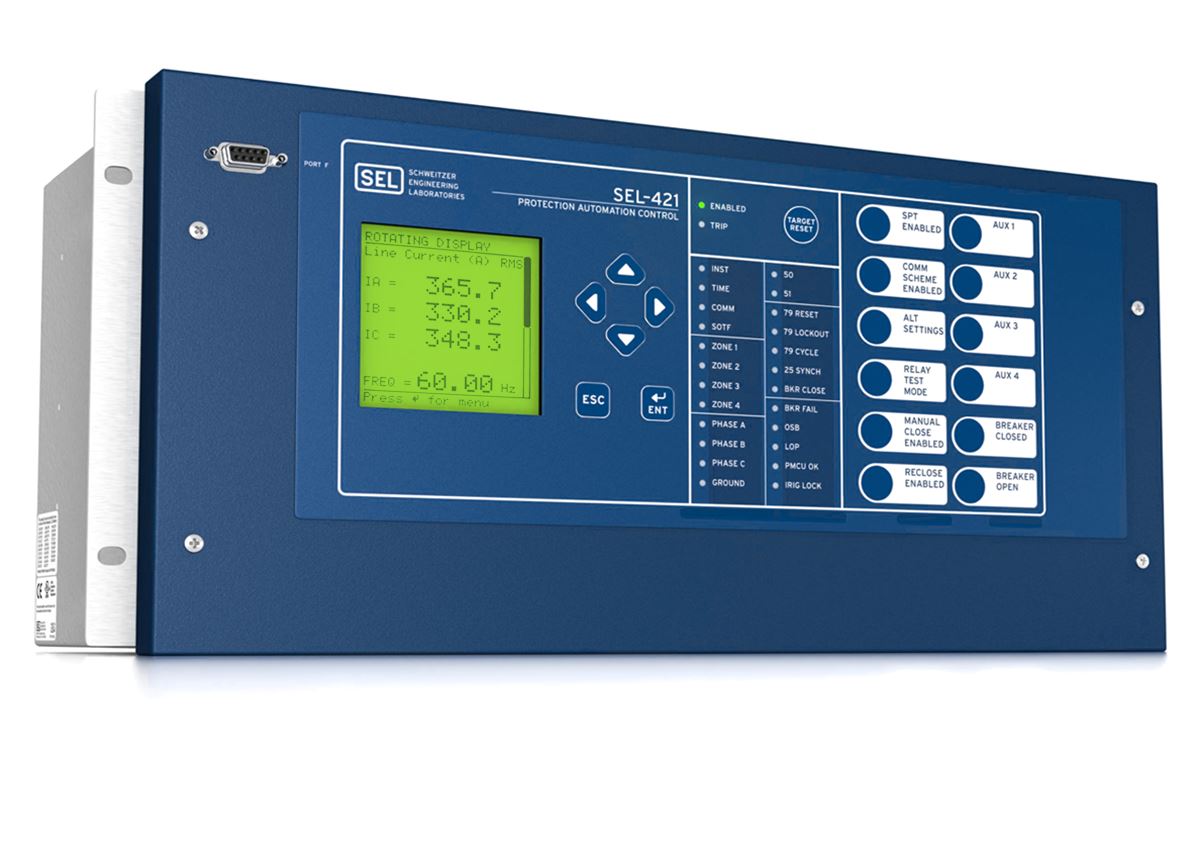
Protection relays
Power system protection relays integrated with real time simulators perform relaying action and supports various communication protocols such as DNp3 and IEC 61850. This allows testing the relays' interoperability.

Network simulators
It adds a "cyber" layer to the setup providing a holistic cyber-physical testbed with real-time co-simulation capabilities.



And more
Real-time automation, programmable logic controllers, phasor measurement units, and smart meters.